Research in Non-Destructive Strain Measurement
Background
Residual stress or strain in engineering components
is one of the most important factors influencing their fatigue life in high
stress applications. Inaccurate prediction of residual stress fields resulting
from either the service loading e.g. mechanical and thermal loading or due to
manufacturing processes e.g. grinding, surface treatment etc. than therefore
significantly influence the components life with catastrophic consequences e.g.
for aerospace industry. It is therefore critical to evaluate these residual
stress fields non-destructively such that the components performance can be
predicted.
Current Research
The aim of the existing research is to investigate
the influence of residual stress profiles on the failure modes of engineering
materials. Influence of manufacturing process on conventional steel components,
as well as the influence of surface treatment such as sprayed (thermally
sprayed) or vapour deposited (Physical Vapour Deposition). Typical example of
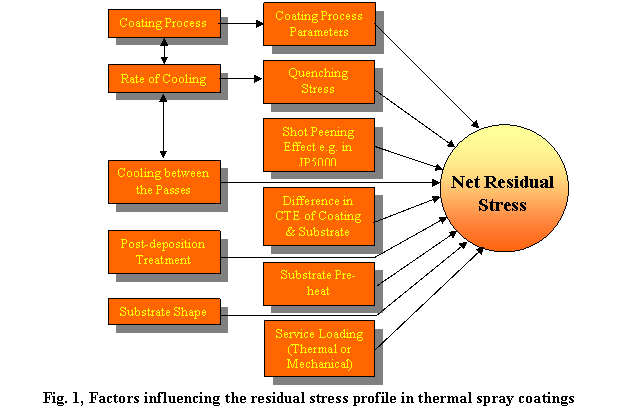
the factors influencing the residual strain in thermal spray coatings can be
appreciated from the schematic shown in Figure 1 below.
Residuals strain measurements have been performed
using conventional x-rays, high energy x-rays, and neutrons. Use of facilities
such as the Daresbury and Rutherford Laboratories,
Experimental results obtained from such experimental
analysis are thus incorporated in numerical (or mathematical) models to predict
components life or failure modes. Some typical experimental results can be
appreciated from the list of
publications and also from the enclosed ISIS
report.